What if, instead of taking a pill or talking with your therapist, you could train your brain to be healthier through a video game? Brain training is becoming increasingly more popular through using a technique called neurofeedback, which allows individuals to change the way their brains function by responding to personalized feedback about how their own brains work naturally. This is one approach being used to treat those struggling with neurological or psychiatric disorders, such as children diagnosed with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), who have difficulty focusing their attention. We now know that a focused brain acts differently than an unfocused brain. Researchers and clinicians are currently investigating whether we can use neurofeedback training to help children induce a “focused” brain state
How can we detect brain activity?
There are two very widely used, non-invasive techniques that detect different aspects of brain functioning: electroencephalography (EEG) and functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) (Figure 1).
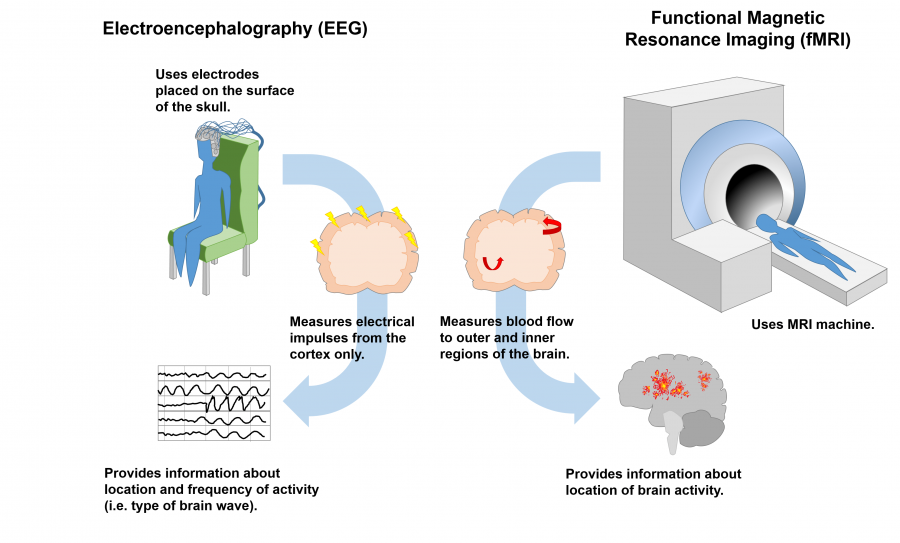
Figure 1. Neurofeedback commonly makes use of two technologies to obtain information about brain function. Electroencephalography (EEG, left) uses electrodes placed on the scalp to detect electrical impulses produced by neurons residing in the outermost layer of the brain, the cortex. Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI, right) measures how much blood flow each region of the brain receives; here, blood flow indicates which regions of the brain are most active.
EEG is a common method by which we can detect brain activity in the cortex, which is the outermost layer of the brain. Activated neurons possess an electrical charge. When groups of neurons are activated at the same time in the same place in the cortex, as occurs during various behavioral or cognitive tasks, the cumulative electrical energy can be detected by electrodes placed on the scalp during an EEG test. These electrical signals are referred to as brain oscillations, or waves. The multiple different kinds of brain waves each represent a different aspect of brain function.
For more articles like this please sign up for our eTips by liking us on Facebook and giving us your email for our Newsletter.





